In human genetics, certain traits are passed down through
the sex chromosomes, which are the X and Y chromosomes. These are
referred to as sex-linked traits and can be either X-linked or Y-linked,
depending on which chromosome carries the gene.
X-Linked Inheritance: When Genes Ride
on the X Chromosome
The X chromosome carries a variety of traits that can be
either recessive or dominant in nature.
X-Linked Recessive Traits
Recessive X-linked disorders
typically appear more often in males than females. This is because males have
only one X chromosome, so a single defective gene on it will express the trait.
In contrast, females need two defective copies to show the condition.
Common examples include:
- Hemophilia
- Red-green
color blindness
How These Traits Are Tracked: The
Pedigree Chart
A pedigree is a diagram that shows how a trait is
inherited across generations:
- Squares
represent males, circles represent females.
- Filled
shapes indicate affected individuals.
- Half-filled
shapes identify carriers—individuals who
carry the gene but do not show the condition.
 |
| Pedigree |
Hemophilia: A Historical and Genetic
Insight
Hemophilia is a rare but serious X-linked
disorder where blood fails to clot properly. Affected individuals bleed
excessively even from minor injuries due to a missing or faulty clotting
factor.
Types of Hemophilia:
- Hemophilia
A & B: X-linked recessive; affect
mainly males.
- Hemophilia
C: Autosomal recessive; affects both sexes equally.
Inheritance Pattern:
Hemophilia A and B are passed from maternal grandfathers
to grandsons through carrier daughters, never directly from father
to son.
 |
| A simplified pedigree showing the X-linked inheritance of haemophilia in European royal family |
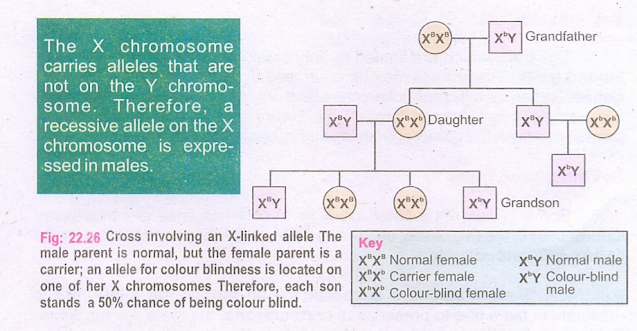
Color Blindness: When the Eyes Miss a
Shade
Color blindness results from mutations in the genes
responsible for color-detecting proteins, called opsins, found in the
eye’s cone cells.
Types of Color Blindness:
- Protanopia:
Red color blindness
- Deuteranopia:
Green color blindness
- Tritanopia:
Blue color blindness (not X-linked)
- Protanomaly
& Deuteranomaly: Partial deficiencies in red and
green perception
- Monochromacy:
Total color blindness; only one type of cone functions
Red-green color blindness is X-linked and more
common in men because they have only one X chromosome. Women must inherit two
defective genes to be color blind.
X-Linked Dominant Inheritance: Traits
That Show Up Even with One Gene
In this case, a single copy of the faulty gene on the X
chromosome is enough to express the trait in both sexes.
Example:
- Brown
teeth — An X-linked dominant trait that can affect males and
females. If the gene is homozygous, all offspring are affected; if
heterozygous, only half may show the trait.
 |
| Hairy Pinnae |
Y-Linked
Inheritance: Passed Only From Father to Son
Y-linked traits are carried on the Y chromosome, so
only males can inherit and express them.
Example:
- Hair
growth on ears — A trait exclusively passed from
father to son.
- The
SRY gene, found on the Y chromosome, is responsible for male
development.
Sex-Limited Traits: Traits That Appear
in One Sex Only
These traits may be governed by sex-linked or autosomal
genes but appear only in one sex due to hormonal influence.
Examples:
- Milk
production in females
- Beard
growth in males
Although a woman doesn’t grow a beard, she can still carry
and pass on the gene to her sons.
Sex-Influenced Traits: Genes That
Behave Differently in Males and Females
These traits are not on the sex chromosomes but
behave differently in males and females due to hormonal influence.
Example:
- Pattern
baldness
- Dominant
in men: A heterozygous male becomes bald.
- Recessive
in women: A female must be homozygous to show baldness.
- In
rare cases, a heterozygous woman with a hormonal imbalance (like an
adrenal tumor) may temporarily develop baldness.
Key Insights to Remember
- Males
are more prone to X-linked recessive disorders
because they lack a second X chromosome to mask faulty genes.
- Traits
on the Y chromosome pass only from father to son and
are never seen in females.
- Sex-limited
and sex-influenced traits are shaped by
hormones and may behave differently in men and women—even if the gene is
the same.
- Pedigree
analysis is a vital tool in identifying
how these traits are passed down through generations.
- Some
traits like color blindness and hemophilia have significant
historical and medical relevance and continue to be key areas of genetic
research.
No comments:
Post a Comment